What Is Functional Medicine?
Have you ever experienced a situation where your healthcare provider tells you that you are perfectly healthy, yet you continue to feel sick? That is because conventional healthcare prioritizes addressing symptoms via medication rather than the underlying causes. In the past 30 years, a new approach to disease management has been rapidly evolving, and it continues to do so.
Keep reading to learn more about functional medicine, a patient-centered approach that aims to uncover the root causes of your condition by taking into consideration your personal history and current lifestyle choices.
History of Functional Medicine
Functional medicine emerged from the insights of a group of influential thinkers who realized that tailoring disease treatments to each individual's unique needs was crucial. They tapped into cutting-edge research in nutrition, genetics, and epigenetics. Their approach sought to address the root causes of illnesses using low-risk interventions that modify molecular and cellular systems to reverse the drivers of disease.
These pioneers achieved remarkable results for patients who had previously struggled with unsuccessful treatments. They accomplished this by returning to fundamental scientific principles and searching for common factors at the cellular and system levels underlying widespread health problems.
As more people showed interest in learning about functional medicine, it became necessary to streamline the approach to teach it to a broader range of healthcare providers.
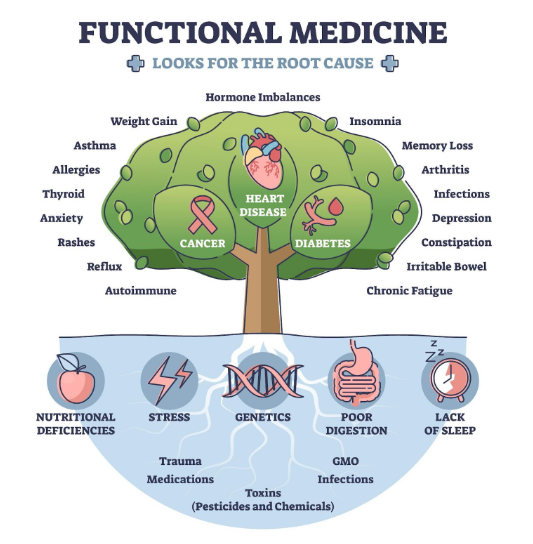
The Overview of the Model
Functional medicine dives deep into understanding why illnesses occur and how to restore health by tackling the root causes of diseases unique to each individual. It views health and illness as a continuum where all aspects of your body interact dynamically with the environment, creating changing patterns and effects over time. Think of it as a clinical application of systems biology.
What Is Systems Biology?
Systems biology is an interdisciplinary field of science that focuses on studying complex biological systems as integrated and interconnected networks of various components, such as genes, proteins, molecules, and cells, rather than individual isolated components. It seeks to understand the functioning of biological systems by analyzing the interactions and relationships between the different elements within these systems.
Key aspects of systems biology include:
Integration of Data: Systems biologists collect and integrate data from various biological disciplines, including genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and more, to create comprehensive models of biological systems. This data often comes from experimental techniques like DNA sequencing, mass spectrometry, and microarray analysis.
Mathematical Modeling: Mathematical and computational modeling play a crucial role in systems biology. These models allow researchers to simulate and predict the behavior of biological systems under different conditions. They can help uncover the underlying patterns, dynamics, and emergent properties of these systems.
Holistic Approach: Systems biology takes a holistic approach to biology, considering how individual components interact within larger networks and pathways. It aims to understand how changes in one part of the system can affect the entire system.
Emergent Properties: One of the primary goals of systems biology is to identify emergent properties—properties that arise from the interactions of system components and cannot be explained by studying those components in isolation. Emergent properties often provide insights into complex biological phenomena.
How Does Functional Medicine View Diseases?
Most diseases aren't solely determined by genetics. Instead, it's how your genes express themselves that matters, influenced by various factors like your environment, lifestyle, diet, activity levels, social factors, and stress.
Functional medicine directly addresses these influencers and aims to uncover the underlying causes of diseases through a comprehensive approach. It acknowledges that your "environment" extends beyond just physical factors. It includes societal conditions and your interactions with others, too!
By considering all these factors, functional medicine allows clinicians to tailor treatments to your specific needs, fostering a better therapeutic partnership between you and your healthcare provider.
How Does Functional Medicine Work in Practice?
Practitioners of functional medicine have developed concepts and tools to help gather, organize, and gain insights from your medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. This comprehensive approach focuses on:
- Understanding your narrative to empathize with and connect with you.
- Creating an optimal healing environment to strengthen the therapeutic relationship.
- Identifying lifestyle and environmental factors that affect your health.
- Using tools like timelines and matrices to map imbalances and key events.
- Integrating this information to uncover the root causes of your health problems and develop personalized recommendations.
Nutrition Is Key
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in functional medicine. Your treatment plan may include various dietary interventions, lifestyle changes, and nutraceuticals (nutrient supplements). Emphasizing nutrition as a priority is essential in functional medicine.
Depression: A Case Study
For instance, if you've tried multiple antidepressants with no success, functional medicine might explore dietary interventions. Studies suggest a link between diet and mental health. One study found that adhering to a healthy diet over time may protect against recurrent depressive symptoms.
It's worth considering the intake of specific nutrients like vitamin K, zinc (for postpartum depression), magnesium, B vitamins, and vitamin D, which may help reduce the risk of depression or alleviate symptoms. Please note that any information we provide here is not intended for self-diagnosis or self-treatment.
Why Choose Functional Medicine?
Choosing functional medicine empowers you as a patient. It fosters a collaborative, unbiased relationship between you and your practitioner. Your voice matters, and your healthcare journey becomes a partnership focused on your unique needs.
If you are interested in functional medicine,
Dr. David Boynton and his staff are ready to help. Take the first step toward reaching optimal health.
Contact us today for a consultation!









